Introduction
Atorvastatin is a widely prescribed medication belonging to the statin class of drugs. It is primarily used to lower elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attacks and strokes. Marketed under the brand name Lipitor, among others, atorvastatin is a cornerstone in the treatment of hyperlipidemia and prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
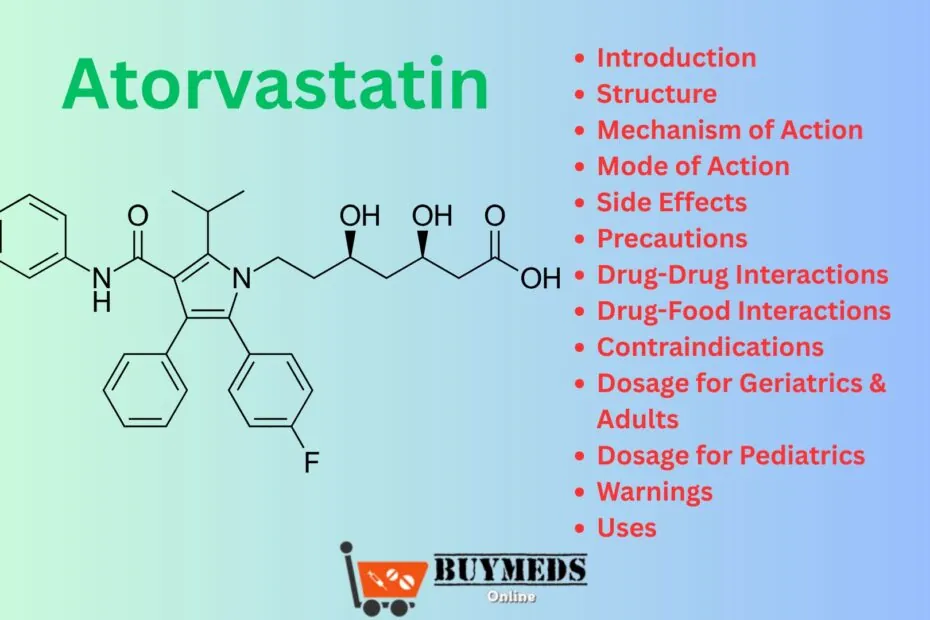
Structure
Atorvastatin calcium is a synthetic lipid-lowering agent.
Chemical Formula: C33H35FN2O5
Molecular Weight: 558.64 g/mol
It contains a fluorophenyl group, a pyrrole ring, and a heptanoic acid chain, which are essential for its activity.
Mechanism of Action
Atorvastatin inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme responsible for converting HMG-CoA to mevalonate, a precursor in the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway. By blocking this enzyme, atorvastatin reduces hepatic cholesterol production, leading to upregulation of LDL receptors in the liver and increased clearance of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) from the bloodstream.
Mode of Action
After oral administration, atorvastatin is absorbed and undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism. It exerts its action primarily in the liver, the target organ for cholesterol reduction. The onset of action is seen within 3–5 days, with the maximal effect typically achieved within 2–4 weeks of consistent use.
Side Effects
Common side effects include:
-
Headache
-
Diarrhea
-
Joint pain
-
Nausea
-
Muscle aches (myalgia)
Serious but rare side effects:
-
Rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle breakdown)
-
Liver enzyme abnormalities
-
Memory impairment
-
Hypersensitivity reactions
Precautions
-
Monitor liver function before and during treatment.
-
Use caution in patients with a history of liver disease or alcohol use.
-
Avoid in patients with unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases.
-
Not recommended during pregnancy and lactation.
-
Dose adjustment may be required in renal impairment.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Atorvastatin interacts with several medications, especially those that inhibit CYP3A4, increasing the risk of side effects:
-
Macrolide antibiotics (e.g., clarithromycin)
-
Azole antifungals (e.g., ketoconazole)
-
Protease inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir)
-
Cyclosporine
-
Gemfibrozil – increases risk of myopathy
-
Digoxin, oral contraceptives – levels may increase with atorvastatin
Drug-Food Interactions
-
Grapefruit juice inhibits CYP3A4 and can increase plasma levels of atorvastatin, raising the risk of side effects.
-
Alcohol should be limited due to potential liver toxicity.
-
High-fat meals may reduce the drug’s effectiveness slightly.
Contraindications
-
Hypersensitivity to atorvastatin or any excipient
-
Active liver disease or unexplained elevated liver enzymes
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
-
Severe hepatic impairment
Dosage for Geriatrics & Adults
Initial dose: 10–20 mg once daily
Maximum dose: 80 mg once daily
Start with a low dose in elderly patients (≥65 years) and titrate based on response and tolerability. Monitor liver function regularly.
Dosage for Pediatrics
Approved for use in children aged 10 years and older:
-
Initial dose: 10 mg once daily
-
Maximum dose: 20 mg once daily (may go up to 80 mg in specific familial hypercholesterolemia cases)
Warnings
-
Risk of myopathy increases with higher doses and certain drug interactions.
-
Monitor CK (creatine kinase) levels in patients with muscle symptoms.
-
Liver enzyme tests are recommended at baseline and periodically during treatment.
-
Discontinue immediately if pregnancy is detected.
-
Use with caution in those with renal dysfunction or thyroid disorders.
Uses
-
Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease
-
Treatment of hypercholesterolemia (especially high LDL-C)
-
Mixed dyslipidemia
-
Homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
-
Hypertriglyceridemia
-
Adjunct to diet in pediatric patients with familial hypercholesterolemia
Expert Advice
-
Take the medication at the same time every day, preferably in the evening.
-
Continue with a low-fat, heart-healthy diet.
-
Inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking.
-
Avoid grapefruit products while on atorvastatin.
-
Report any muscle pain, weakness, or yellowing of the skin to a doctor immediately.
-
Do not stop taking atorvastatin without consulting your healthcare provider.
FAQs
Q1: Is atorvastatin safe for long-term use?
Yes, when taken as prescribed and monitored regularly, atorvastatin is safe and effective for long-term use in managing cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular disease.
Q2: Can I take atorvastatin at any time of the day?
Though it can be taken any time, it’s often recommended in the evening because cholesterol synthesis in the liver is higher at night.
Q3: What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed one. Do not double the dose.
Q4: Can atorvastatin be stopped abruptly?
No, stopping suddenly may result in a rebound increase in cholesterol levels. Always consult your physician before discontinuation.
Q5: Does atorvastatin affect kidney function?
It generally does not affect the kidneys, but rare cases of rhabdomyolysis can lead to kidney damage. Prompt recognition of muscle symptoms is essential.
Frequent Search Terms: Atorvastatin, Lipitor, statins, cholesterol medication, atorvastatin dosage, atorvastatin side effects, atorvastatin uses, atorvastatin interactions, atorvastatin in children, atorvastatin precautions.