Introduction
Chlorhexidine is a broad-spectrum antiseptic and disinfectant used for skin disinfection before surgery and for sterilizing surgical instruments. It is widely utilized in mouthwashes to reduce dental plaque and oral bacteria. As a potent antibacterial agent, chlorhexidine plays a vital role in infection prevention across medical, dental, and personal hygiene settings.
Drug Class: Antiseptic, Disinfectant
ATC Code: D08AC02 (topical use), A01AB03 (oral use)
Common Forms: Mouthwash, solution, gel, cream, swab, and wipes
Structure
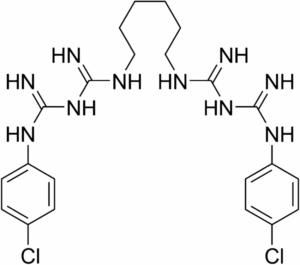
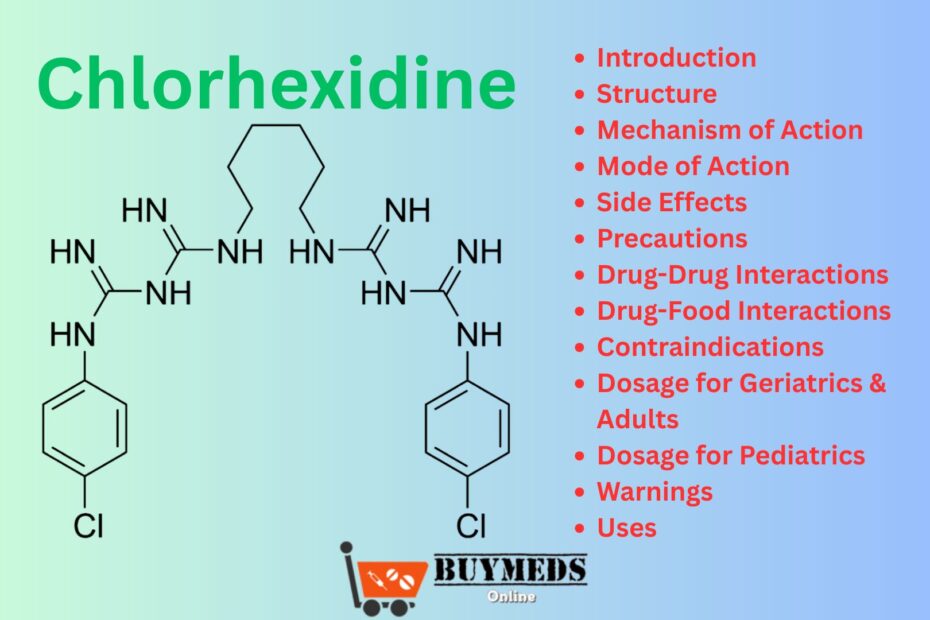
Chemical Name: 1,1′-Hexamethylenebis[5-(p-chlorophenyl)biguanide]
Molecular Formula: C22H30Cl2N10
Molecular Weight: 505.45 g/mol
Chlorhexidine is typically available as chlorhexidine gluconate or chlorhexidine acetate in its salt form, which enhances solubility in aqueous solutions.
Mechanism of Action
Chlorhexidine disrupts the bacterial cell membrane’s integrity. It binds to negatively charged bacterial cell walls, causing leakage of intracellular components. At lower concentrations, it has bacteriostatic effects, and at higher concentrations, it is bactericidal.
Mode of Action
-
Initial Binding: Positively charged chlorhexidine molecules bind to negatively charged sites on bacterial cell walls.
-
Membrane Disruption: This interaction destabilizes the membrane, increases permeability, and leads to leakage of potassium and phosphorus.
-
Cell Death: At higher doses, chlorhexidine causes precipitation of cytoplasmic contents, leading to irreversible cell death.
Side Effects
Though generally well-tolerated, chlorhexidine can cause the following side effects:
-
Common:
-
Oral staining (brown discoloration of teeth/tongue with mouthwash)
-
Taste alteration
-
Dryness or burning sensation
-
-
Less Common:
-
Skin irritation or redness
-
Allergic reactions
-
-
Rare but Serious:
-
Anaphylactic reactions (especially with intravenous or surgical prep formulations)
-
Precautions
-
Avoid contact with eyes and ears, especially during surgical preparations.
-
Do not swallow chlorhexidine mouthwash.
-
Not for prolonged use without medical supervision.
-
Patch test is recommended before using skin formulations in sensitive individuals.
-
Caution in patients with asthma or respiratory sensitivity to aerosolized solutions.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Chlorhexidine has minimal systemic absorption, so interactions are rare. However:
-
May be inactivated by anionic compounds like sodium lauryl sulfate found in many toothpastes.
-
Avoid using simultaneously with other antiseptics like iodine, as they may neutralize each other.
Drug-Food Interactions
-
No significant food interactions.
-
For oral rinses, avoid eating or drinking immediately after use to maximize local efficacy.
Contraindications
Chlorhexidine is contraindicated in:
-
Known hypersensitivity or allergy to chlorhexidine or its components
-
Use in the auditory canal (risk of ototoxicity)
-
Use in the eyes (can cause corneal damage)
Dosage for Geriatrics & Adults
-
Oral Rinse (0.12% or 0.2%): Rinse with 10–15 mL for 30 seconds twice daily
-
Topical Application: Apply thin layer to the affected skin area 1–3 times daily
-
Preoperative Skin Prep (2–4%): Use as directed before surgical procedures
No specific dose adjustment required for geriatric patients, but skin sensitivity may increase with age.
Dosage for Pediatrics
-
Mouthwash: Not typically recommended for children under 6 years due to the risk of swallowing
-
Topical Use: Safe under medical supervision in older children
-
Pediatric use should always be guided by a healthcare provider.
Warnings
-
May stain dental surfaces and restorations with long-term use.
-
Not intended for internal use or injection.
-
Use with caution in pregnancy and breastfeeding—generally considered safe topically or as a rinse.
-
Risk of severe allergic reactions—discontinue immediately if symptoms occur.
Uses
-
Oral Care: Treatment of gingivitis, plaque control, post-dental surgery care
-
Skin Antiseptic: Preoperative skin disinfection
-
Hand Disinfectant: Used by healthcare professionals for hand hygiene
-
Wound Care: Prevention of infection in minor cuts, burns, and abrasions
-
Catheter and Device Antisepsis: Reduces microbial contamination risk
Expert Advice
-
Brush teeth before using chlorhexidine mouthwash to avoid interaction with toothpaste.
-
Do not dilute or rinse with water after using the oral solution.
-
Store chlorhexidine-containing products away from light and heat.
-
Use with care on broken or inflamed skin to prevent irritation.
-
Report any signs of allergy (rash, difficulty breathing, swelling) immediately.
FAQs
1. Is chlorhexidine safe for daily use?
Yes, when used as directed and not for prolonged periods without supervision.
2. Can I use chlorhexidine with toothpaste?
Avoid using toothpaste immediately before or after chlorhexidine mouthwash. Wait at least 30 minutes.
3. Does chlorhexidine kill viruses?
It is primarily antibacterial, but may have some limited activity against enveloped viruses.
4. Is it safe during pregnancy?
Topical and oral use is generally safe during pregnancy. Always consult your doctor before use.
5. What should I do if I accidentally swallow chlorhexidine?
Seek medical advice, especially if large amounts are ingested.
Frequent Search Terms: Chlorhexidine, Chlorhexidine gluconate, Chlorhexidine uses, Chlorhexidine mouthwash, Chlorhexidine side effects, Chlorhexidine dosage, Antiseptic mouthwash, Chlorhexidine precautions, Chlorhexidine drug interaction, Pharmacist drug guide.