Introduction
Fluocinolone is a synthetic corticosteroid used topically or via intraocular implants to treat various inflammatory and allergic conditions. As a potent glucocorticoid, it exhibits strong anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties. It is most commonly available as Fluocinolone acetonide, a derivative formulated for enhanced efficacy and stability.
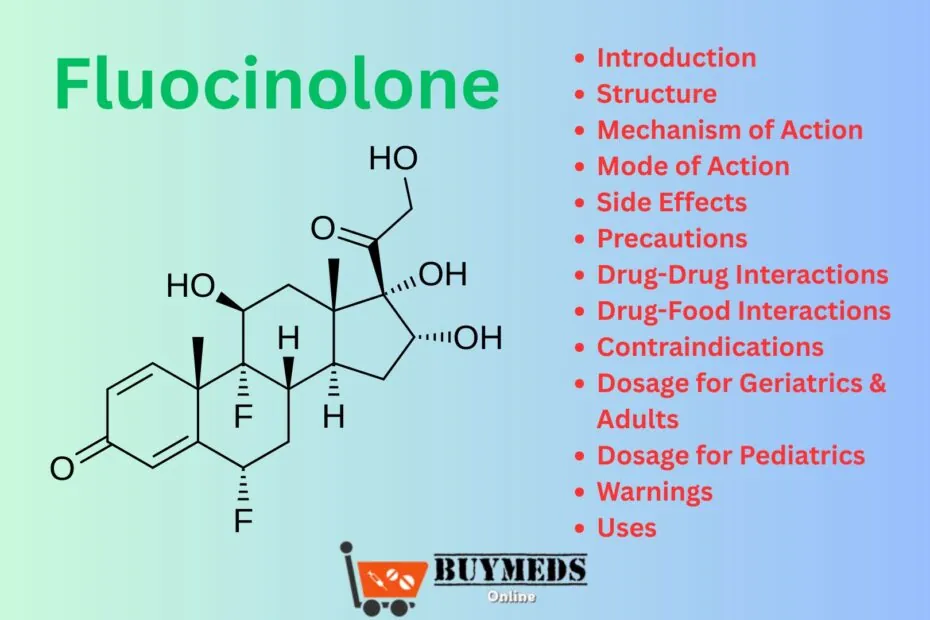
Structure
Chemical Name: Fluocinolone
Molecular Formula: C21H26F2O6
Molecular Weight: 412.430 g/mol
Mechanism of Action
Fluocinolone binds to glucocorticoid receptors in the cytoplasm, forming a complex that translocates into the nucleus. This complex modulates gene transcription, inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukins and TNF-α while promoting anti-inflammatory proteins like lipocortin.
Mode of Action
Anti-inflammatory Effect: Inhibits phospholipase A2 activity, reducing prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
Immunosuppressive Action: Suppresses immune cell migration and activity at the inflammation site.
Vasoconstrictive Property: Reduces capillary permeability, minimizing edema and erythema.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects (Topical):
Burning or stinging sensation
Skin dryness or irritation
Itching or redness
Less Common:
Skin thinning
Hypopigmentation
Acneiform eruptions
Stretch marks (striae)
Intraocular Implant Side Effects:
Increased intraocular pressure
Cataract formation
Eye pain or discomfort
Vision changes
Precautions
Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration.
Avoid contact with eyes unless specifically formulated for ophthalmic use.
Do not apply to open wounds or infected skin.
Monitor intraocular pressure with ophthalmic use.
Use with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Systemic absorption can occur, especially with prolonged use on large surface areas.
Drug-Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase systemic corticosteroid levels.
Ritonavir and similar protease inhibitors may enhance corticosteroid effects.
Concomitant use with other corticosteroids increases the risk of systemic effects.
May reduce the effectiveness of live vaccines.
Drug-Food Interactions
Not significantly affected by food when used topically or ophthalmically.
Systemic absorption (rare) may require dietary sodium control in hypertensive patients.
Avoid alcohol if systemic side effects appear.
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to fluocinolone or any component of the formulation.
Untreated bacterial, fungal, or viral infections of the skin (e.g., herpes simplex, varicella).
Ocular use is contraindicated in viral diseases of the cornea and conjunctiva.
Dosage for Geriatrics & Adults
Topical Formulations:
Apply a thin layer to the affected area 2–4 times daily.
Maximum duration: usually 2–4 weeks unless otherwise directed.
Intraocular Implant (e.g., for diabetic macular edema):
0.19 mg implant, administered via intravitreal injection.
Duration: sustained release for up to 36 months.
Dosage for Pediatrics
Use with caution due to risk of systemic absorption and growth suppression.
Apply the minimum effective dose, typically no more than twice daily.
Avoid occlusive dressings in children unless advised by a healthcare professional.
Warnings
Prolonged use may lead to adrenal suppression and Cushing’s syndrome.
Discontinue use if irritation or allergic reaction occurs.
Monitor for ocular hypertension with intraocular implants.
Avoid in pregnancy (Category C) unless benefits outweigh risks.
Uses
Dermatologic: Eczema, psoriasis, lichen planus, allergic dermatitis
Ophthalmic: Chronic non-infectious uveitis, diabetic macular edema (DME)
Oral/Scalp Preparations: Aphthous ulcers, scalp psoriasis
Expert Advice
Always apply thinly to affected skin—more does not mean better.
For ophthalmic use, follow exact instructions and avoid contamination of the applicator.
Wash hands before and after application unless treating hands.
Do not use for more than 2 weeks without medical supervision.
Avoid applying to the face, groin, or underarms unless specifically prescribed.
FAQs
Q1. Is Fluocinolone a steroid?
Yes, it is a corticosteroid, specifically a glucocorticoid.
Q2. Can I use Fluocinolone on my face?
Only under medical supervision. The skin on the face is more sensitive and prone to side effects.
Q3. Is Fluocinolone safe during pregnancy?
It falls under Category C. Use only if clearly needed and prescribed.
Q4. Can Fluocinolone cause skin thinning?
Yes, prolonged use can lead to atrophy or thinning of the skin.
Q5. How long does the intraocular implant last?
The intravitreal implant can release medication for up to 36 months.