Introduction
Neomycin is a broad-spectrum aminoglycoside antibiotic primarily used to reduce the risk of bacterial infections. It is most commonly applied topically or taken orally for specific conditions, including hepatic encephalopathy and to suppress gut flora before surgery. Due to its potent antibacterial properties, Neomycin plays a critical role in both hospital and outpatient settings, though its systemic use is limited due to toxicity risks.
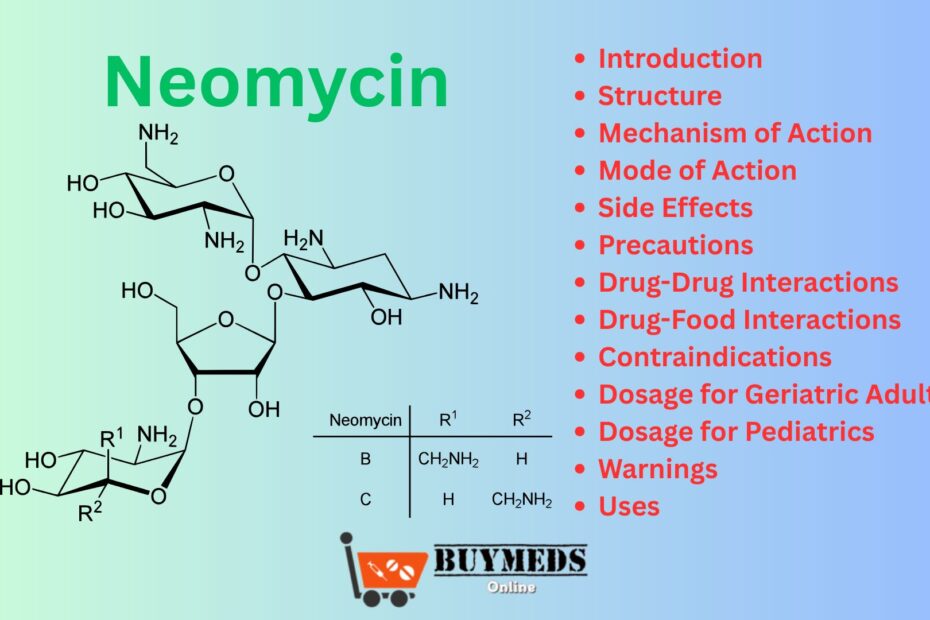
Structure
Neomycin is a complex compound comprising a mixture of Neomycin B and Neomycin C, with Neomycin B being the major component. It belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics, chemically characterized by:
-
Multiple amino sugars
-
A hexose ring linked via glycosidic bonds
-
High polarity and water solubility
Molecular Formula: C23H46N6O13
Molecular Weight: ~614.6 g/mol
Mechanism of Action
Neomycin binds irreversibly to the 30S ribosomal subunit of susceptible bacteria, causing a disruption in protein synthesis. This misreading of mRNA leads to the production of nonfunctional or toxic proteins, ultimately causing bacterial cell death. Its action is bactericidal, making it effective against a wide range of Gram-negative and some Gram-positive organisms.
Mode of Action
Neomycin exhibits a concentration-dependent killing mechanism. Once inside bacterial cells, it:
-
Inhibits the initiation complex of protein synthesis
-
Causes incorporation of incorrect amino acids
-
Leads to cell membrane damage
However, due to poor oral absorption, its systemic use is limited. When taken orally, it acts locally in the gastrointestinal tract.
Side Effects
Neomycin, particularly in systemic or high-dose use, can lead to serious side effects:
-
Nephrotoxicity (kidney damage)
-
Ototoxicity (hearing loss or balance issues)
-
Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling)
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Diarrhea or gastrointestinal discomfort
-
Superinfections with prolonged use
Precautions
Before using Neomycin:
-
Assess for kidney impairment, as the drug can accumulate and cause toxicity.
-
Monitor hearing in long-term or high-dose usage.
-
Caution in patients with neuromuscular disorders such as myasthenia gravis.
-
Avoid concurrent use with other ototoxic or nephrotoxic drugs.
-
Not recommended during pregnancy, unless absolutely necessary.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Neomycin may interact with:
-
Loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide): Increased risk of ototoxicity
-
Other aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin): Increased toxicity
-
Neuromuscular blocking agents: Enhanced muscle paralysis
-
Methotrexate or Digoxin: Altered absorption or serum levels
Drug-Food Interactions
-
Oral Neomycin may have reduced efficacy if taken with high-fat meals.
-
Alcohol may irritate the GI tract and should be avoided during treatment.
-
Probiotic use may be recommended after therapy to restore gut flora.
Contraindications
Neomycin is contraindicated in:
-
Hypersensitivity to Neomycin or other aminoglycosides
-
Pre-existing hearing loss
-
Intestinal obstruction
-
Severe renal impairment
-
Pregnancy (Category D – risk to the fetus)
Dosage for Geriatrics & Adults
-
Oral (hepatic coma): 4 to 12 g/day in divided doses
-
Preoperative bowel preparation: 1 g every hour for 4 doses, then 1 g every 4 hours (total: 6-8 g/day)
-
Topical use: Apply a thin layer to the affected area 1-3 times daily
Note: Renal function should guide dosing adjustments.
Dosage for Pediatrics
-
Oral: 50-100 mg/kg/day in divided doses
-
Topical: Apply a small amount to the affected area 1-3 times daily
Pediatric dosing must be closely monitored due to the risk of systemic absorption and toxicity.
Warnings
-
BLACK BOX WARNING (for systemic use): May cause nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and ototoxicity.
-
Monitor renal function and auditory health during prolonged use.
-
Avoid concurrent use with similar toxic agents.
-
Not intended for long-term or large-area topical use, especially in infants or patients with broken skin.
Uses
Neomycin is used for:
-
Preoperative bowel sterilization
-
Hepatic encephalopathy (to reduce ammonia-producing bacteria)
-
Topical infections (minor cuts, burns, or wounds)
-
Component in triple antibiotic ointments
-
Adjunctive therapy in GI infections
Expert Advice
-
Do not use Neomycin on large wounds or broken skin unless directed.
-
Avoid prolonged use due to risk of sensitization and resistance.
-
Ensure adequate hydration to protect kidneys.
-
Inform your doctor if you have any hearing difficulties or kidney disease.
-
Complete the full course of the antibiotic as prescribed.
FAQs
Q1. Can Neomycin be taken orally?
Yes, but it is poorly absorbed and used primarily to treat intestinal infections or reduce gut bacteria before surgery.
Q2. Is Neomycin safe during pregnancy?
Neomycin is not recommended during pregnancy, particularly due to the risk of fetal hearing loss.
Q3. What should I do if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not double up.
Q4. Can Neomycin cause hearing loss?
Yes. Ototoxicity is a serious risk, especially with prolonged or high-dose use. Any hearing changes should be reported immediately.
Q5. Can Neomycin be used for acne?
It may be included in topical formulations, but it’s not a first-line acne treatment due to resistance concerns.
Frequent Search Terms: neomycin, neomycin uses, neomycin dosage, neomycin side effects, neomycin interactions, neomycin for adults, neomycin for children, neomycin precautions, neomycin warnings, aminoglycoside antibiotic.